Projects
DeepPVMapper
DeepPVMapper is a deep learning-based mapping algorithm developed to map rooftop PV installations over France.
GitHub repository | Project website
The Github repository is accessible here.
Click here
to download the minimum data (images, model weights, additional data) to replicate the example provided in the
Github repository.
The list of publications associated with the paper are accessible here:
- Kasmi, G., Dubus, L., Blanc, P., & Saint-Drenan, Y. M. (2022). Towards unsupervised assessment with open-source data of the accuracy of deep learning-based distributed PV mapping. arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.07466.
Wavelet Attribution Method (WAM)
Feature attribution methods aim to improve the transparency of deep neural networks by identifying the input features that influence a model's decision. Pixel-based heatmaps have become the standard for attributing features to high-dimensional inputs, such as images, audio representations, and volumes. While intuitive and convenient, these pixel-based attributions fail to capture the underlying structure of the data. Moreover, the choice of domain for computing attributions has often been overlooked. This work demonstrates that the wavelet domain allows for informative and meaningful attributions. It handles any input dimension and offers a unified approach to feature attribution. Our method, the Wavelet Attribution Method (WAM), leverages the spatial and scale-localized properties of wavelet coefficients to provide explanations that capture both the where and what of a model's decision-making process. We show that WAM quantitatively matches or outperforms existing gradient-based methods across multiple modalities, including audio, images, and volumes. Additionally, we discuss how WAM bridges attribution with broader aspects of model robustness and transparency.
GitHub repository | Project website
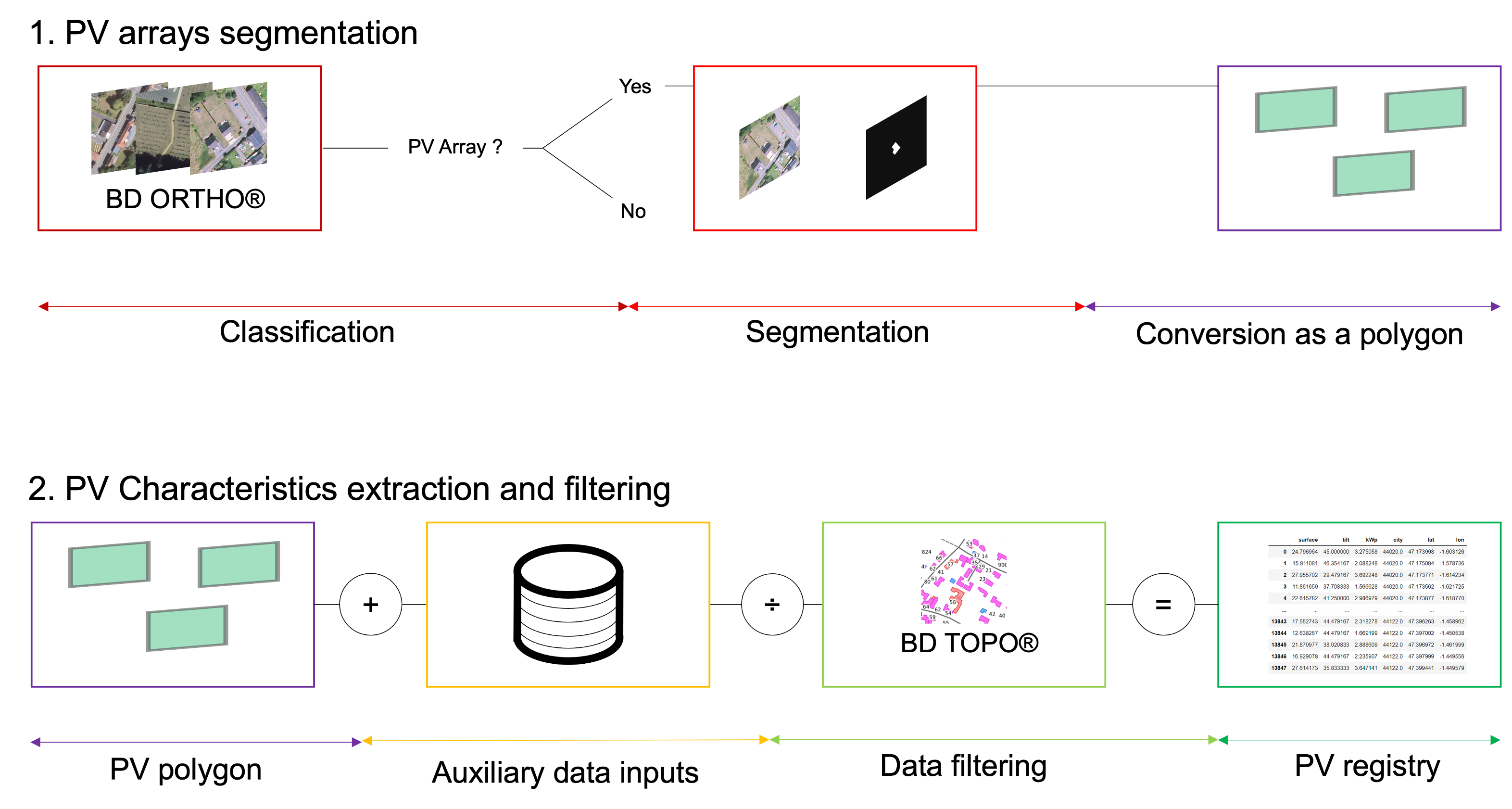
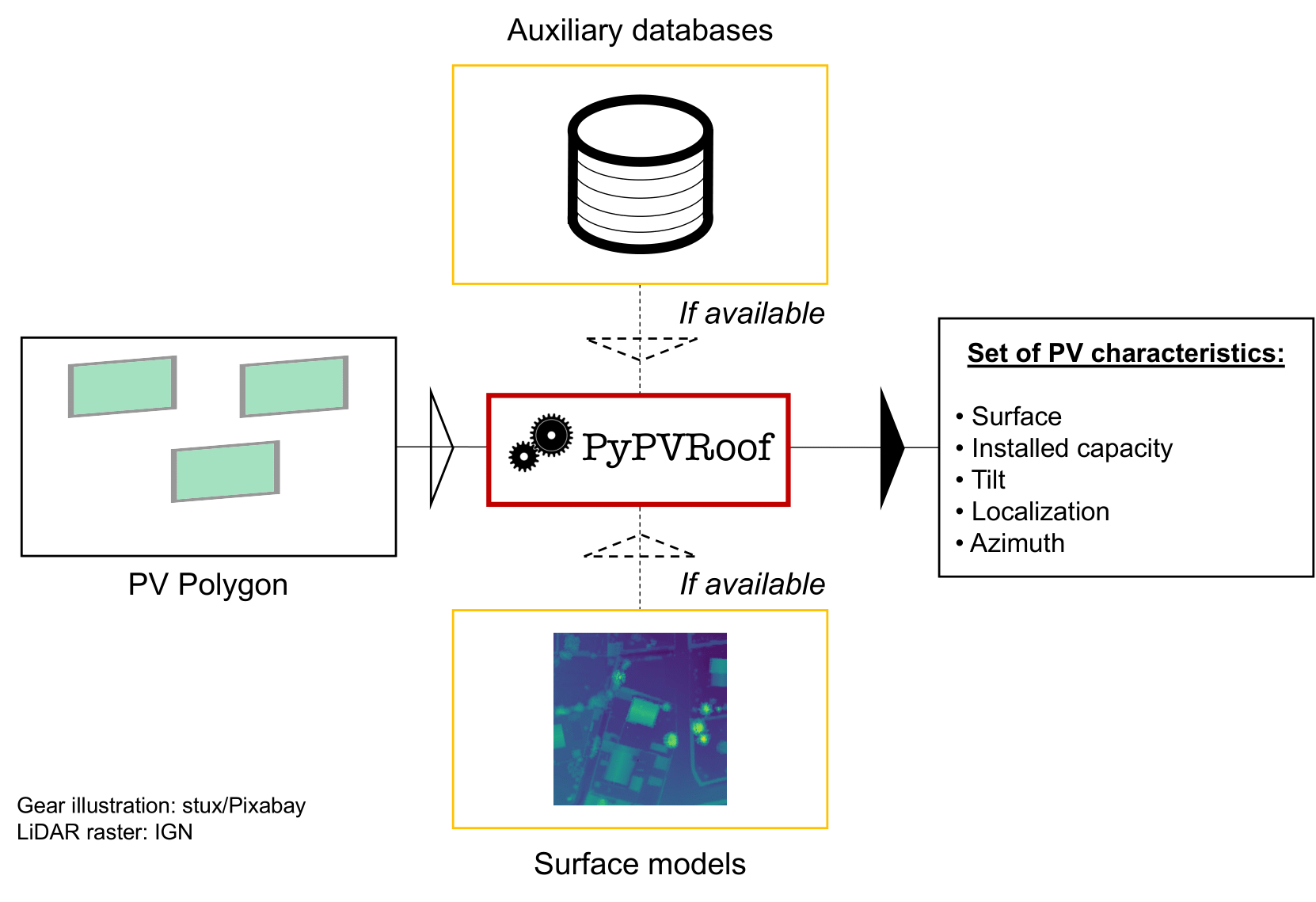
PyPVRoof
PyPVRoof is a Python package to extract essential PV installation characteristics. These characteristics are tilt angle, azimuth, surface, localization, and installed capacity.
PyPVRoof is designed to cover all use cases regarding data availability and user needs and is based on a benchmark of the best existing methods. The package is designed to be used in a Jupyter notebook or in a Python script. It can be used with or without additional data (3D LiDAR data, additional registry). The package is designed to be used with Python 3.7 or higher.
The current version is available on PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/pypvroof/.
Photovoltaic (PV) energy grows at an unprecedented pace,
which makes it difficult to maintain up-to-date and accurate PV registries,
which are critical for many applications such as PV power generation estimation.
This lack of qualitative data is especially true in the case of rooftop PV installations.
As a result, extensive efforts are put into the constitution of PV inventories.
However, although valuable, these registries cannot be directly used for monitoring
the deployment of PV or estimating the PV power generation, as these tasks usually
require PV systems characteristics. To seamlessly extract these characteristics
from the global inventories, PyPVRoof. PyPVRoof is a Python package to extract essential
PV installation characteristics. These characteristics are tilt angle, azimuth,
surface, localization, and installed capacity. PyPVRoof is designed to cover all use
cases regarding data availability and user needs and is based on a benchmark of the
best existing methods. Data for replicating our accuracy benchmarks are available
on our Zenodo repository,
and the package code is
accessible on our Github repository.
The supporting preprint is accessible here:
- Trémenbert, Y., Kasmi, G., Dubus, L., Saint-Drenan, Y. M., & Blanc, P. (2023). PyPVRoof: a Python package for extracting the characteristics of rooftop PV installations using remote sensing data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07143.